During the nineteenth century Torquay’s population increased from around 800 to almost 34,000. The town became a place for the wealthy to buy holiday homes, the retired to reside, and the sick to hopefully recover from their illnesses. In the late 1840s we were connected to the rail network which brought thousands of holiday-makers needing accommodation in hundreds of hotels and boarding houses.
By the end of the century Torquay claimed to have 500 villas housing a new affluent middle class. They were eager to demonstrate their status and position in society and used a variety of methods. One of these was to cultivate a garden.
Having a garden could offer flowers for decoration and a place for leisure activities. Alongside providing everyday foods, the innovative gardener could also offer unheard of luxuries. For example, we still have the remains of Lauriston Hall’s Orangery, the idea being to display wealth and the ability to grow exotic fruits in an unsuitable climate. 
It was at this time of enthusiasm for gardening that many of the familiar names of today were founded. Suttons Seeds, for instance, was founded in Reading in 1806, and relocated to Torquay in 1976; in 1998 it moved again to Paignton.
Torquay became a very rich place and, to maintain and communicate this uniqueness in a competitive market, public parks played an important role. As well as presenting a wealthy and leisured society to both residents and visitors, such spaces expressed scientific knowledge and a healthy activity. They also proclaimed the town’s position as the elite leisure resort at the centre of a vast Empire -an English Riviera.
Torbay’s microclimate further stimulated a demand for trees and plants that could not be easily grown in other parts of the country. The design, construction and maintenance of gardens and parks provided work for hundreds of men and women.
These new villas, hotels, and parks all needed plants and trees and they created a new type of industry – the plant nursery.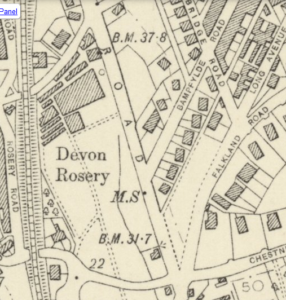
In Torbay there we no nurseries until one was opened around 1831.By 1861 there were 4 nurseries; 6 in 1881; 10 in 1891; and 16 in 1900. Some specialised in a particular type of plant such as Curtis and Sanford’s Devon Rosery who produced roses alongside Avenue Road.
When a head gardener was unable to grow sufficient plants and trees, or a desired type, the plant nursery would produce offer those that home owners, hoteliers and the local authorities might like to purchase. Run by nurserymen, the nurseries also had attractive gardens and glasshouses, designed to attract visitors and customers.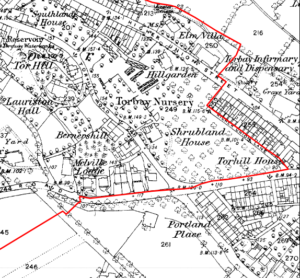
Initially, advertisements were targeted at the wealthy but by the end of the century, they were offering plants to all classes. Torquay was a competitive environment and so the first home to acquire something new could make an impression on society; and attract a better type of guest to the hotels.
Nursery men also designed and advised on the layout of parks and gardens and stocked them with trees, plants, seeds and equipment. These were the days of Empire and, to satisfy an interest in foreign places, they sent explorers abroad to bring back seeds and cuttings from exotic places. 84 Devon nurseries specialised in imported exotics which could be grown in a mild climate.
Bearing in mind that Torquay was a tourist resort catering for Britain’s elite, new species of tropical plants could often be found on sale in the town even before being grown in London. 
These non-British plants and trees also helped to reinforce the idea of Torquay being the English Riviera- foreign but also very English. Even today it’s not uncommon to come across a Monkey Puzzle tree, native to Chile and Argentina, or Bay Trees, Holm Oaks and the Italian Cyprus from the Mediterranean. And, of course, there’s the ubiquitous New Zealand Cabbage Palm.
Many of these Torquay nurseries have disappearing under buildings – several were situated along Avenue Road due to the need to access a water supply.
They are, however, remembered by the names of the thoroughfares that replaced them: Sanford & Co’s Devon Rosery’s legacy in Rosery Road; while Morgan’s Nursery is remembered in Morgan Avenue.


























